Magnetism of Topological Boundary States Induced by Boron Substitution in Graphene Nanoribbons
Physical Review Letters - 2020
Niklas Friedrich*, Pedro Brandimarte*, Jingcheng Li, Shohei Saito, Shigehiro Yamaguchi, Iago Pozo, Diego Peña, Thomas Frederiksen, Aran Garcia-Lekue, Daniel Sánchez-Portal, and Jose Ignacio Pascual* N.F. and P.B. contributed equally
Abstract
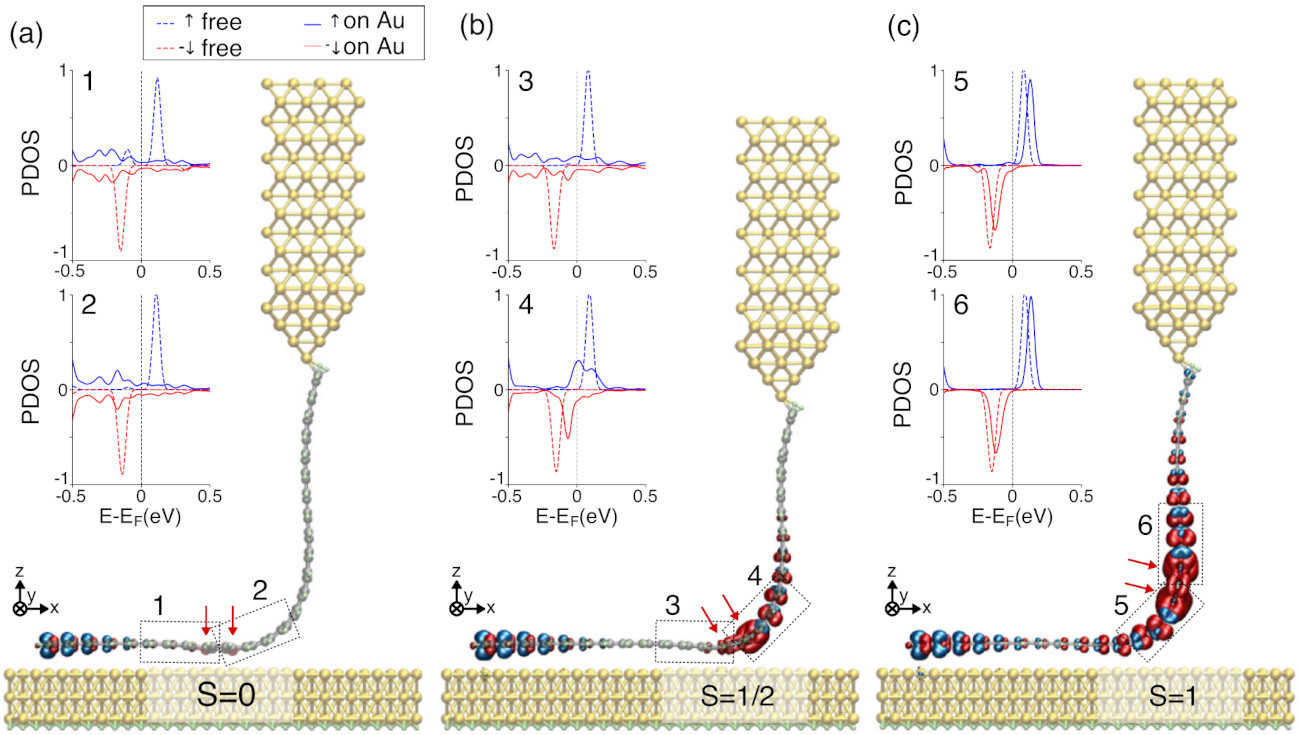
Graphene nanoribbons (GNRs), low-dimensional platforms for carbon-based electronics, show the promising perspective to also incorporate spin polarization in their conjugated electron system. However, magnetism in GNRs is generally associated with localized states around zigzag edges, difficult to fabricate and with high reactivity. Here we demonstrate that magnetism can also be induced away from physical GNR zigzag edges through atomically precise engineering topological defects in its interior. A pair of substitutional boron atoms inserted in the carbon backbone breaks the conjugation of their topological bands and builds two spin-polarized boundary states around them. The spin state was detected in electrical transport measurements through boron-substituted GNRs suspended between the tip and the sample of a scanning tunneling microscope. First-principle simulations find that boron pairs induce a spin 1, which is modified by tuning the spacing between pairs. Our results demonstrate a route to embed spin chains in GNRs, turning them into basic elements of spintronic devices.
Press release
Our work was selected for the cover of Issue 14 of Physical Review Letters 2020:

Our article was discussed at Mapping Ignorance.
Our paper was also highlighted at APS NEWS - November 2020 (Volume 29, Number 10).
Bibtex citation
@Article{Friedrich2020,
author = {Niklas Friedrich and Pedro Brandimarte and Jingcheng Li and Shohei Saito and Shigehiro Yamaguchi and Iago Pozo and Diego Pe{\~{n}}a and Thomas Frederiksen and Aran Garcia-Lekue and Daniel S{\'{a}}nchez-Portal and Jos{\'{e}} Ignacio Pascual},
title = {Magnetism of Topological Boundary States Induced by Boron Substitution in Graphene Nanoribbons},
journal = {Physical Review Letters},
year = {2020},
volume = {125},
number = {14},
pages = {146801},
doi = {10.1103/PhysRevLett.125.146801},
publisher = {American Physical Society},
}
Key words
- electronic structure
- spin polarization
- molecular magnetism
- Kondo effect
- symmetry protected topological states
- graphene nanoribbon
- chemical doping